OUR FOCUS: INVASIVE FUNGAL INFECTIONS
Combating fungal disease—a global imperative
Fungal pathogens are responsible for at least 13 million infections and 1.5 million deaths globally every year. While most healthy people can naturally fight off these pathogens, fungi are opportunistic—taking advantage of hosts with suppressed or compromised immune systems. These include people undergoing treatment for cancer, those receiving immunosuppressive drugs following an organ or stem cell transplant, and people with autoimmune or inflammatory diseases. Other risk factors for invasive fungal infections include liver failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and severe infection due to COVID-19 and influenza.

We are working to help fulfill a vast unmet need for physicians and patients facing the threat of invasive fungal infections.

The economic burden of invasive fungal infections
Hospital admissions for an invasive fungal infection are estimated to cost the US healthcare system
$0 billion
USD ANNUALLY
Invasive fungal infections diagnosed during a hospital stay cost an additional
$0 billion
PER YEAR in the US alone
The World Health Organization has highlighted the critical need for new antifungal therapies, especially for hard-to-treat fungi like Mucorales and Aspergillus species, as well as emerging pathogens and drug-resistant species of Candida.
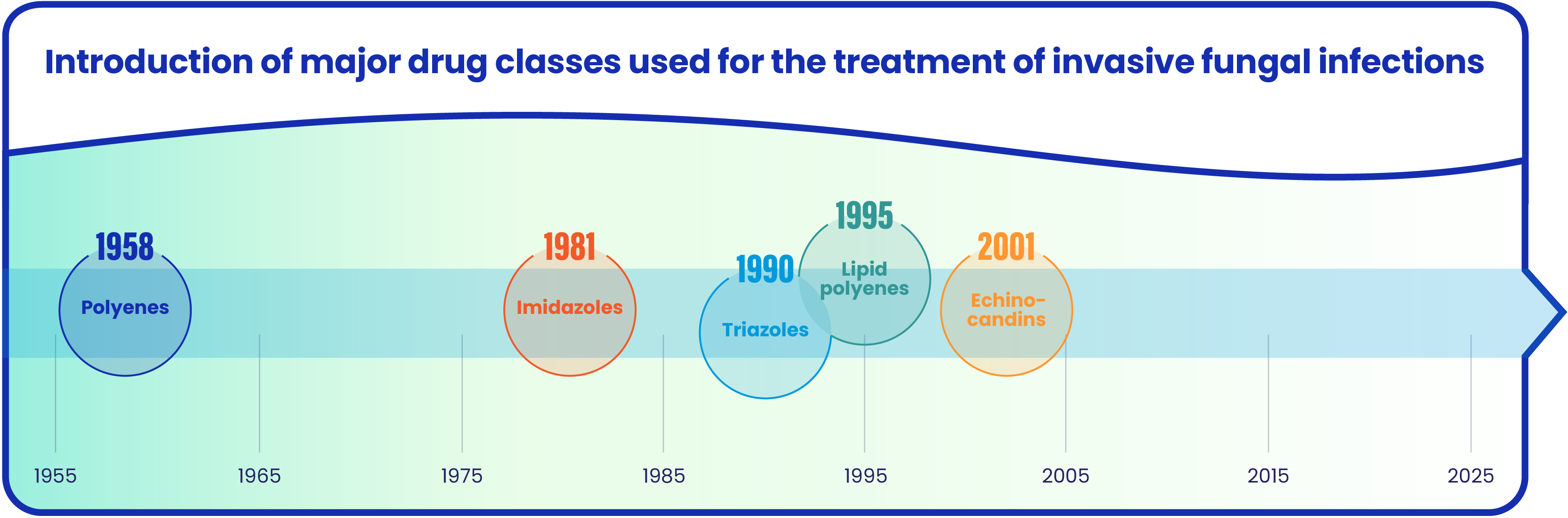
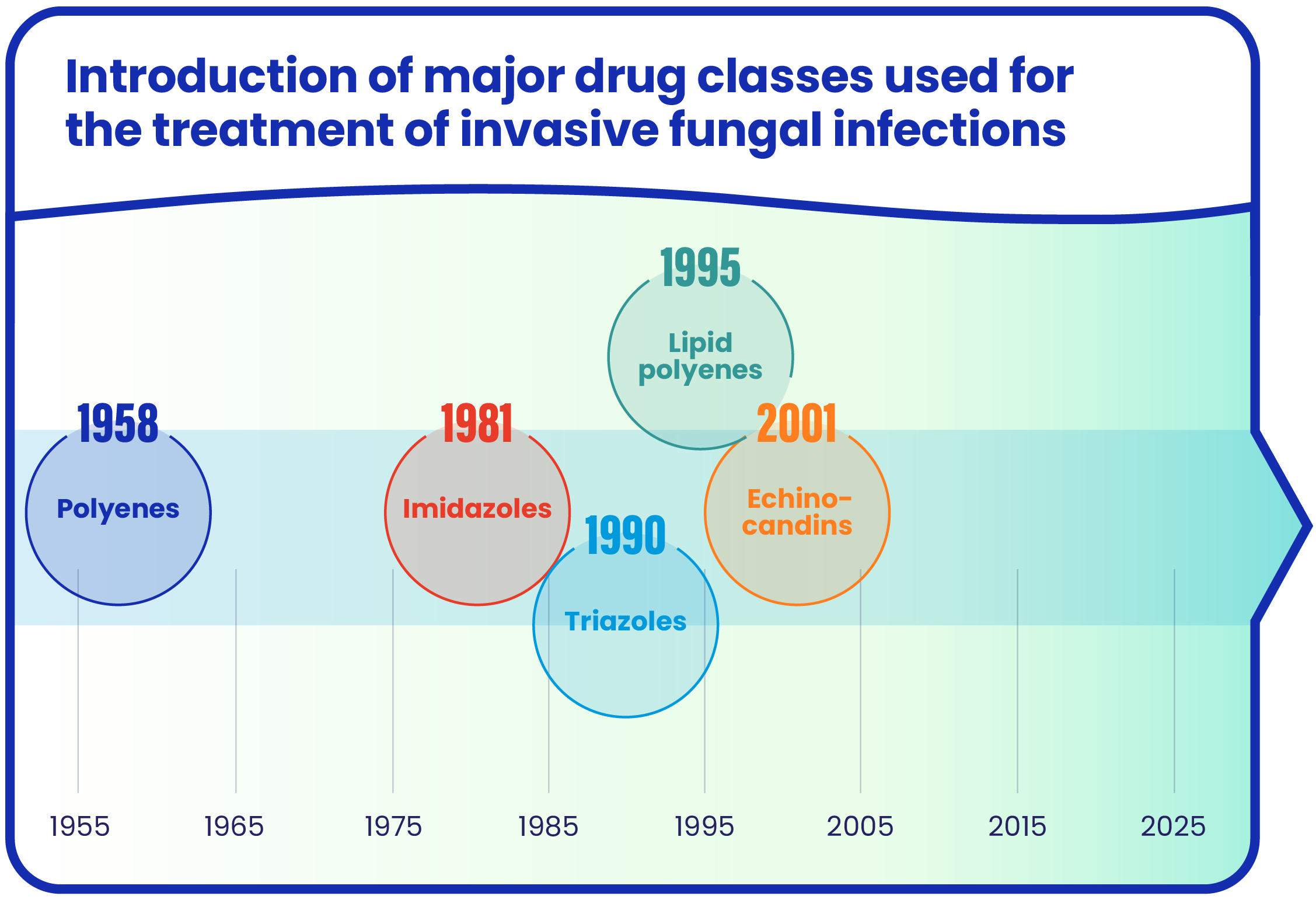
The past and current treatment landscape
Elion Therapeutics was founded on the understanding that mechanistic insights enable the targeted optimization of natural products. We hold this conviction at the core of our clinical development of the next-generation polyene SF001.
Polyene antifungals were introduced in the 1950s. The first one, amphotericin B, quickly became widely known for its efficacy but also for its systemic toxicities, including severe renal toxicity. Later, lipid formulations were developed to mitigate against these toxicities, but they were only moderately safer.
Since then, other classes of anitfungals have been introduced in the ongoing fight against invasive fungal infections. Nevertheless, challenges and unmet needs remain, underscoring the importance of continued drug development in the antifungal treatment landscape.